This chapter provides orientation on the Workflow module, a tool that allows information to be shared and various event-related activities to be monitored and queried. These events can be understood as any occurrences that need to be monitored, which may include tasks, actions, problems, processes, requests, and issues. The Workflow module provides a single point of contact, allowing for effective communication among those involved in the events. The main benefits of this methodology include a reduced response time; standardized, centralized, and organized information; and event-related metrics.
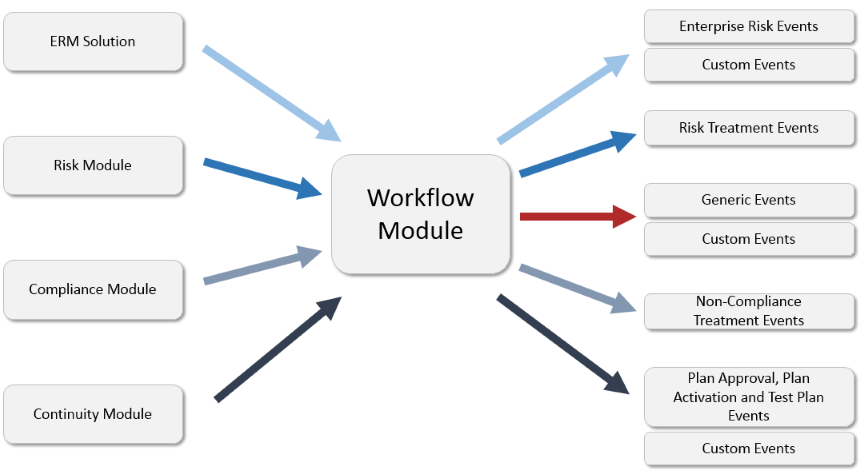
The flexibility of this module allows it to handle various types of events (see figure below).

Through the Workflow module, you can monitor events of the following types:
•Generic events: Events of this type are created in the Workflow module itself to monitor any type of activity. For details on creating events of this type, see Chapter 10: Workflow -> Events -> Creating Generic and Custom Events.
•Risk treatment events: Events of this type (which are divided into two subtypes – Control or Vulnerability) do not require manual registration, since they are generated during the Evaluation phase in risk projects. These are designed to monitor activities related to implementing one or more controls from knowledge bases or treating vulnerabilities. For details on creating events of this type, see Chapter 5: Risk -> Risk Management Projects -> Risk: The Evaluation Phase.
•Non-compliance treatment events: Events of this type do not require manual registration, since they are generated during the Evaluation phase in compliance projects. These are designed to monitor activities related to fulfilling requirements from one or more authoritative documents. For details on creating events of this type, see Chapter 6: Compliance -> Compliance Projects -> Compliance: The Evaluation Phase.
•Business continuity events: The Plan Approval, Plan Activation, and Test Plan event types are available by default with the installation of the Continuity module. For details, see Chapter 11: Continuity -> Continuity Module Configurations.
•Enterprise risk events: If the ERM solution is installed, the Enterprise Risk Event type will also be available as a default event type. For details, see Chapter 4: ERM -> Risk Register -> Manage Enterprise Risks -> How to Create an Event with an Associated Enterprise Risk.
•Custom event types: New types of events, other than those listed above, can be created in the Object Types section of the Administration module. These may include events to monitor customer support requests, manage incidents, or resolve tickets, for example. Once custom event types are created, they will be available for selection when creating events in the Workflow module by selecting an option from the Event Type field. Custom events can also be created through the ERM solution and the Continuity module if they are installed and if associations with enterprise risks and continuity plans is enabled for the event types used. For details on creating event types, see Chapter 17: Administration -> Customizations -> Object Types. For details on creating events of this type, see Chapter 10: Workflow -> Events -> Creating Generic and Custom Events.
Keep in mind that events of all types can be associated with system objects and with each other. In addition, events can also have other events registered beneath them. For details on associating events, see Chapter 10: Workflow -> Events -> Event Associations with Objects and Chapter 10: Workflow -> Events -> Associating and Disassociating Events.
In the Administration module, you can also customize the layouts of specific event types, create new tabs, as well as restrict the permissions received by system profiles and Workflow roles in each tab. For details, see Chapter 17: Administration -> Customizations -> Event Layouts.
The Queries section provides a wizard to guide you through each step of the process of creating customized queries to view information on events, which can be displayed by event, by date, by asset, or by event progress. This information can be filtered by specific properties of the events – such as their status, USR score, event type, attributes, and others. Once generated, these results can be viewed through tables, by default, or by maps, if a location was registered for at least one event in the scope of the query.
In the Treemap section, a query can be created to view a map with boxes of different sizes and colors, each of which represents a specific event. This query can be filtered to only show a certain type of event and only a certain number of events. The sizes and colors of the boxes will vary according to the indicators selected. This feature provides a graphic overview of the events to which you have permission, according to the configurations selected.