This topic explains how to create a query to view risk indicators for authoritative documents and requirements mapped to controls analyzed in risk projects. These mappings can be displayed by control status and requirement or be consolidated by authoritative document, requirement, or by requirement and control. These results always display the most recent information from risk analyses, considering the latest closed questionnaires. This means that if the same asset component is analyzed in more than one project, its analysis results will only display the risk indicators obtained from the latest closed questionnaire. Information from other projects will not be included in these results.
1. Access the Risk module.
2. Select List Queries from the Queries section.
3. In the Project Queries section, click Create.
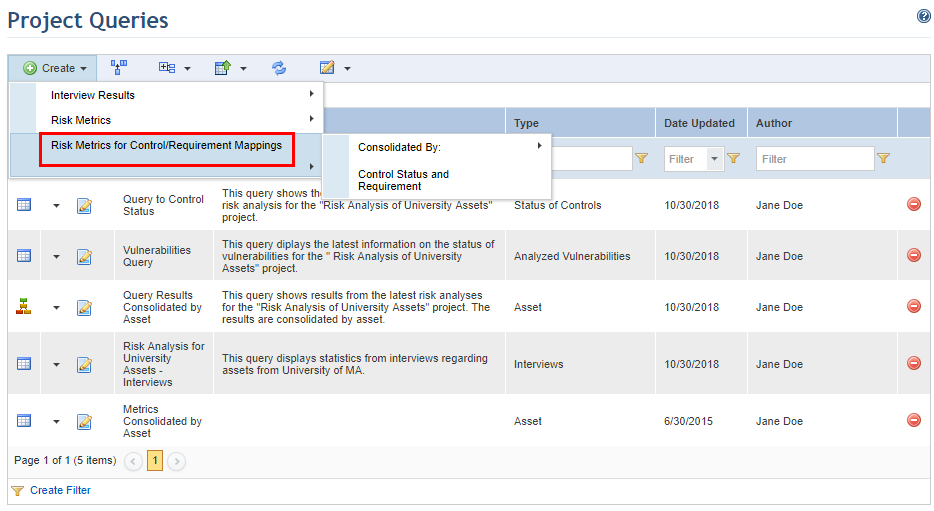
4. Expand Risk Metrics for Control/Requirement Mappings (see figure below).

5. Select the Control Status and Requirement option, or click Consolidated By and select one of the available options.
Note: Each type of query displays the latest risk analysis results for the option selected, as detailed below:
•Control Status and Requirement: This option displays risk indicators for requirements mapped to controls that were analyzed in the risk projects selected in the scope of the query. Data on each control analyzed in the projects will be displayed, with details on its relationships with requirements. Note that results from different projects are displayed separately, which may generate multiple entries for the same object. For example, if a control was mapped to a requirement and this control was analyzed four times in different projects, the query will display the results and information for this control and requirement four times, one for each occurrence.
•Authoritative Document: This option displays risk indicators consolidated for the authoritative documents whose requirements were mapped to controls analyzed in the risk projects selected in the scope of the query. This consolidation counts the number of times a requirement and any of its child requirements are associated with a control. For example:
Requirement 005.001.001 is mapped to a non-implemented control X whose PSR score is 125
AND
Requirement 005.001 is not associated with any control
AND
Requirement 005 is associated with a non-implemented control Y with a PSR score of 125
THEN
PSR score for the authoritative document will be 250
•Requirement: This option displays risk indicators consolidated for the requirements that were mapped to controls analyzed in the risk projects selected in the scope of the query. This consolidation counts the number of times child requirements were associated with controls. If parent requirements have not been associated with any controls, they will display the results for their child requirements. Using the example above, requirement 005.001 would have a PSR score of 125, since it was not directly associated with any controls and thus only displays the results for its child requirement 005.001.001. Requirement 005 would have a PSR score of 250, since it would include its own PSR score of 125 plus the PSR score of its child requirement 005.001.001. By default, this query is grouped by authoritative document and by requirement.
•Requirement and Control: This option displays the same results as the Requirement query (above), except that it also displays all the controls associated with the requirements and the number of times these controls were analyzed. In the Requirements query, on the other hand, only the requirements are displayed, even if their results were obtained from two different controls mapped to them and regardless of the number of times they were analyzed.
For example, in this query, if a control associated with a requirement was analyzed four times in risk projects (twice as implemented and twice as not implemented), the four responses to this control will be taken into consideration. The Risk Index in this case would be 50% and the Security Index would be 50%. By default, this query is grouped by requirement and by authoritative document.
The system displays the Scope step in the wizard for creating queries, where the assets and perimeters from which information will be obtained can be selected (see figure below).
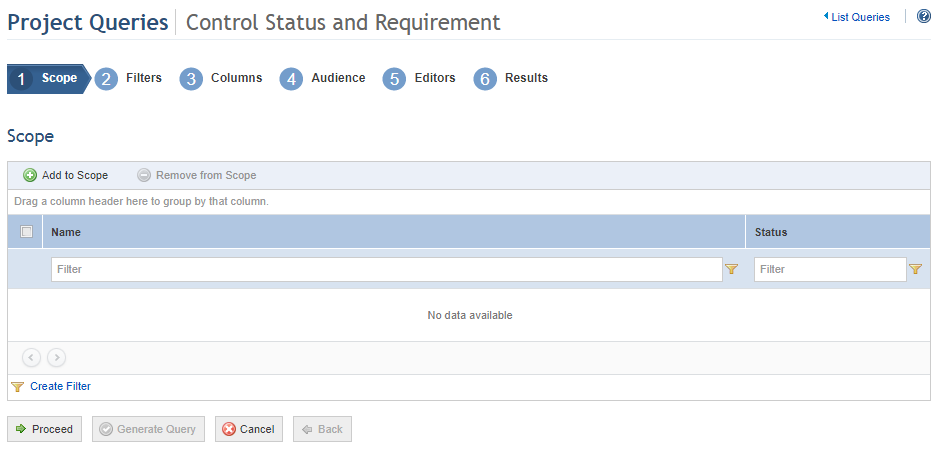
6. Click Add to Scope to select the projects to be included in the scope.
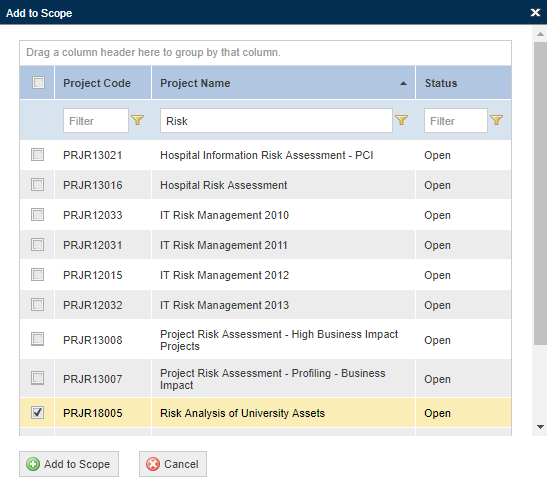
The system displays a list containing the list of open and closed risk projects registered in the system. Cancelled projects are not listed.
7. Select the projects you want to include in the scope by marking the checkboxes next to each and clicking Add to Scope (see figure below). If you want to quit the operation, click Cancel.
8. To remove an item from the scope, mark the checkbox next to it and click Remove from Scope.
9. When finished, click Proceed to continue creating the query. If you want to run the query, click Generate Query. If you want to quit the operation, click Cancel.
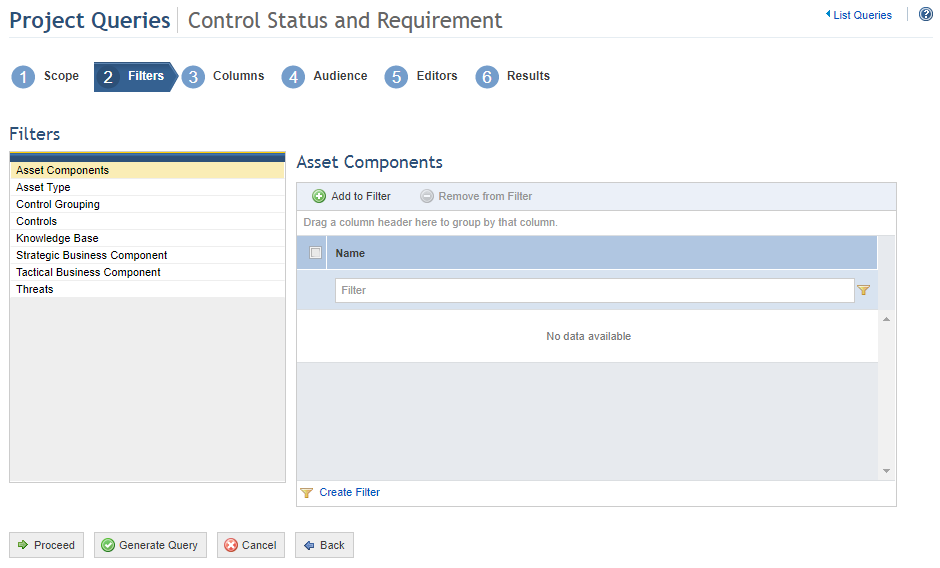
When Proceed is clicked, the system displays the Filters step in the wizard for creating the query, where the filters to be used can be selected, which will reduce the information used to display the results (see figure below).
Note: Risk metrics are always consolidated based on the controls, since this is the most granular object that can be analyzed in a project. Requirements inherit risk indicators from the controls to which they are mapped. Selecting a filter means indicating that only the controls, and, in turn, the mapped requirements, meeting the criteria set in the filters selected will be displayed in the query results. For example, if you filter the query by a certain knowledge base, only the controls related to that knowledge base will be displayed in the results.
10. Select the filter you want to use by clicking one of the filter options displayed on the left (see figure below).
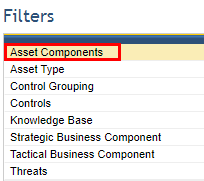
11. Click Add to Filter to select the objects that will be used to filter the scope of the query (see figure below).
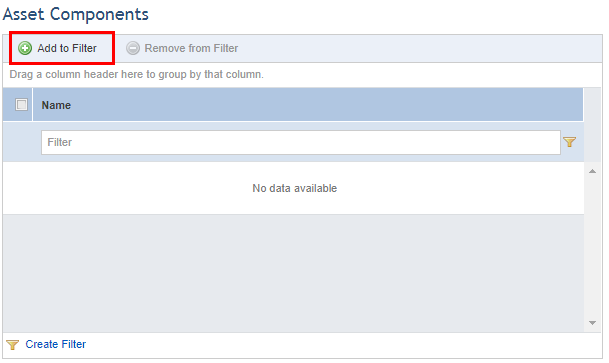
12. Select the objects to be added to the filter in the window that appears and click Add Selected (see figure below). If you want to quit the operation, click Cancel.
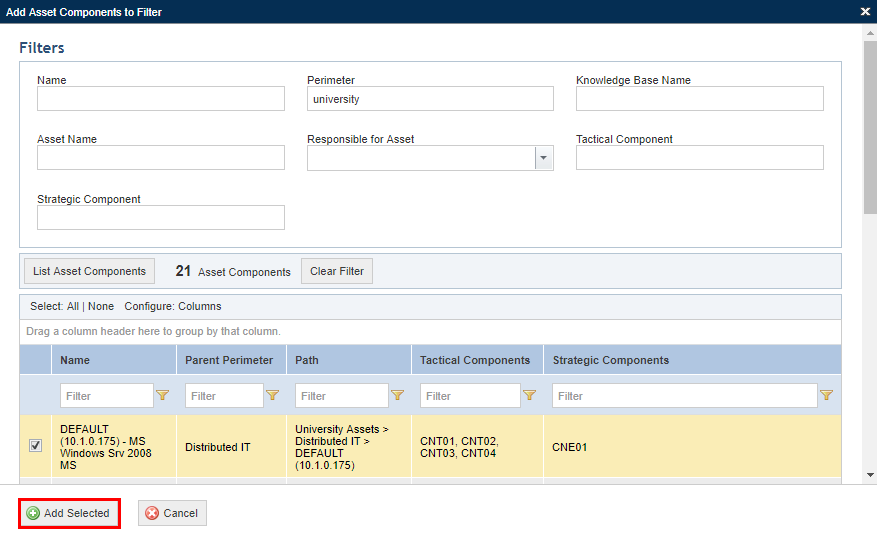
The system displays the objects selected for the filter.
13. To remove objects added to the filter, mark the checkboxes next to each you want to remove and click Remove from Filter.
14. After selecting the filters, click Proceed to continue creating the query. If you want to generate the query, click Generate Query. If you want to cancel query creation, click Cancel. To return to the previous step at any point during this wizard, click Back.
When Proceed is clicked, the system displays the Columns step, where the columns to be displayed in the query results can be selected (see figure below).
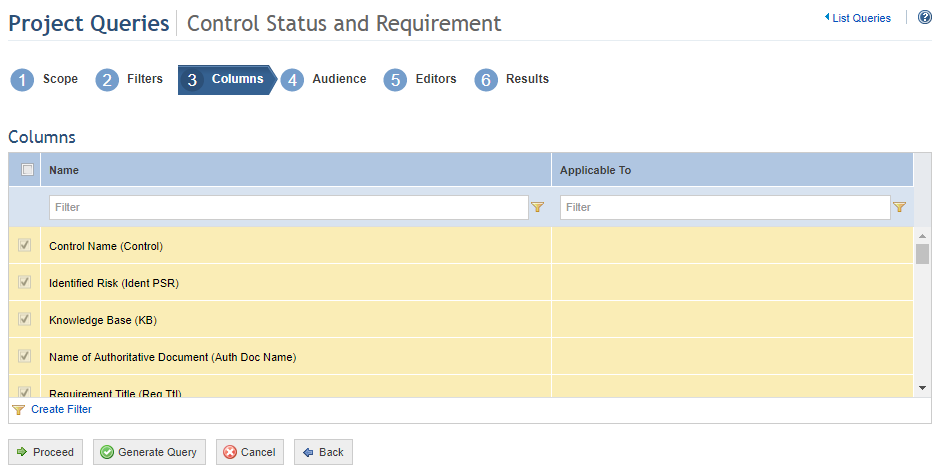
15. Select the columns you want to include in the query by marking the checkboxes next to each. By default, the system will show some pre-selected options that can be removed, while others are required columns. To include or remove optional columns in the results, simply mark or unmark the checkboxes next to their names.
16. Click Proceed to continue creating the query. If you want to generate the query, click Generate Query. If you want to cancel query creation, click Cancel. To return to the previous step at any point during this wizard, click Back.
When Proceed is clicked, the system displays the Audience step, where you can select which people and groups will be able to view the query in the Home module and in this module, if they have permission to access it (see figure below).
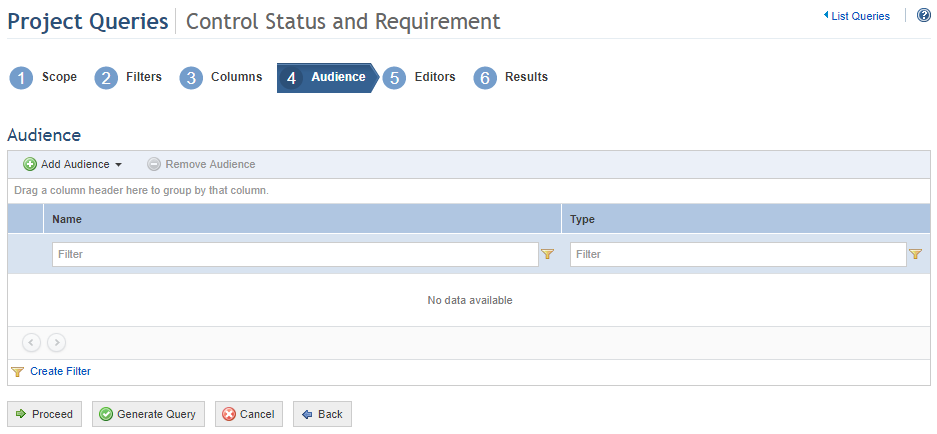
17. Click Add Audience and select People or Groups to add them.
18. If, for example, you selected People, select the people to be added and click Add People (see figure below). If you want to quit the operation, click Cancel.
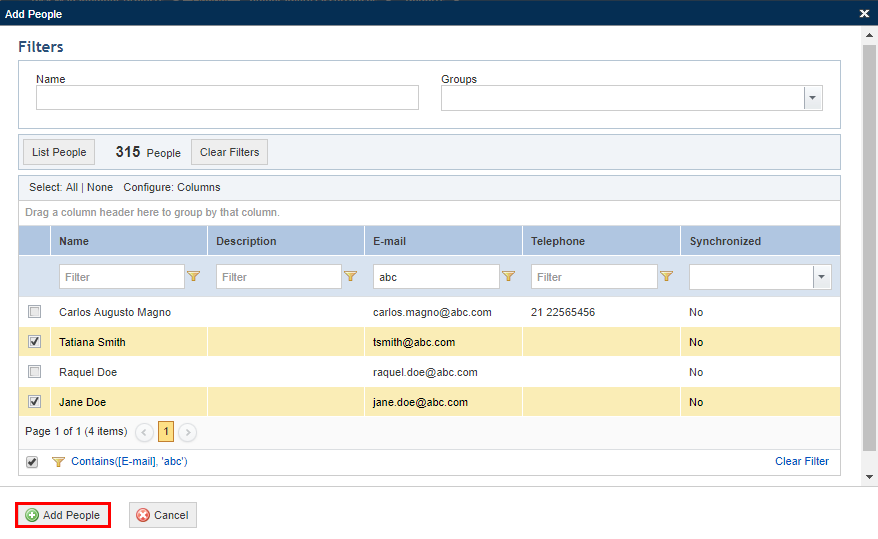
The system displays the people selected.
19. To remove people or groups from the audience, mark the checkboxes next to their names and click Remove Audience.
The system requests confirmation to remove the people or groups from the audience (see figure below).
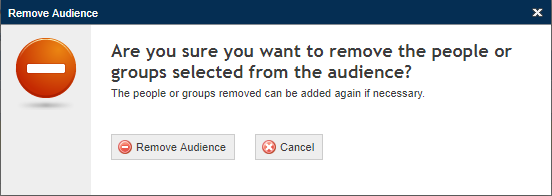
20. Click Remove Audience to confirm. If you want to quit the operation, click Cancel.
The system removes the people selected from the audience.
21. Click Proceed to continue creating the query. If you want to generate the query, click Generate Query. If you want to cancel query creation, click Cancel. To return to the previous step, click Back.
When Proceed is clicked, the system displays the Editors step, where you can select which people and groups will be able to edit the query, receiving the same permissions to it as the author (see figure below).
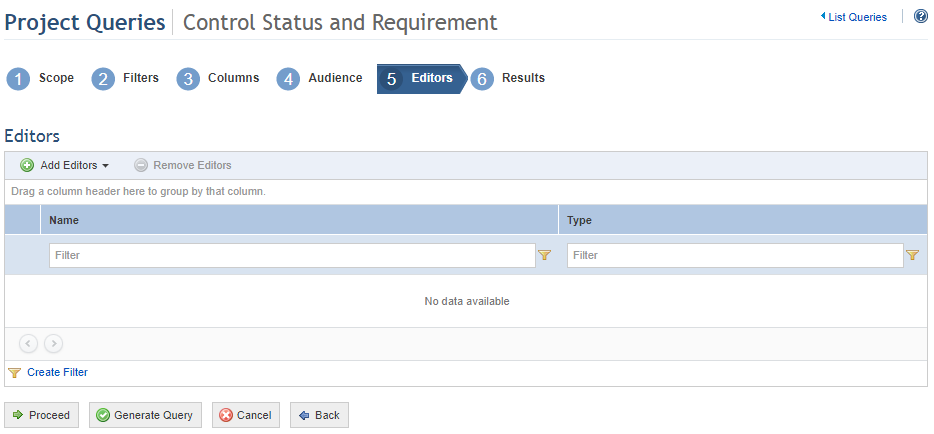
22. Click Add Editors and select People or Groups to add them to the list of editors.
23. If, for example, you selected People, select the people to be added and click Add People (see figure below).

The system displays the people selected.
24. To remove people or groups from the list of editors, mark the checkboxes next to their names and click Remove Editors.
The system requests confirmation to remove the people or groups from the list of editors (see figure below).
25. Click Remove Editors to confirm. If you want to quit the operation, click Cancel.
The system removes the people selected from the list of editors.
26. Click Proceed or Generate Query to run the query. If you want to cancel query creation, click Cancel. To return to the previous step, click Back.
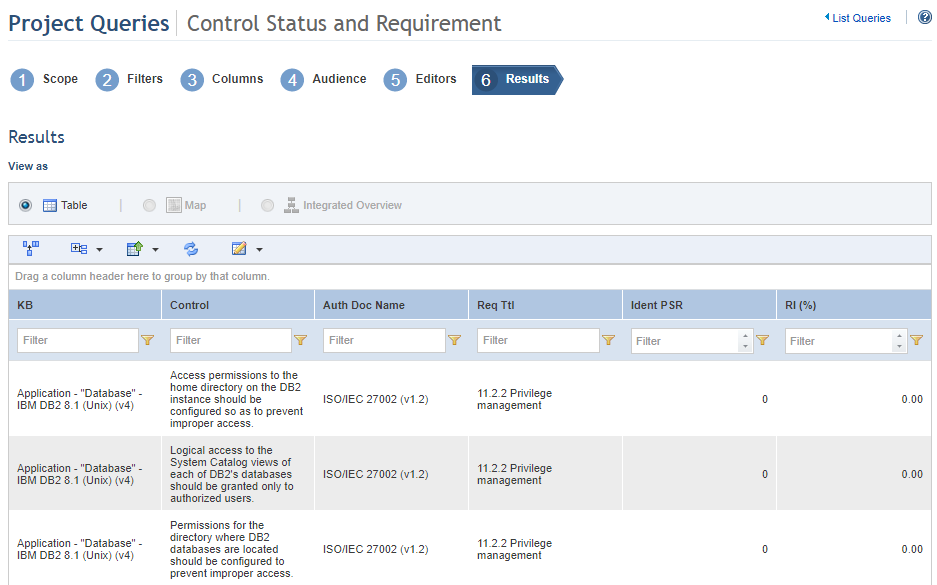
When Proceed is clicked, the system displays the results of the query according to what was selected in the previous steps (see figure below).
27. Click Save to save the query data. If you do not want to save the query, click Cancel. To return to the previous step, click Back.
When Save is clicked, the system displays a window where a name and description for the query can be entered (see figure below).
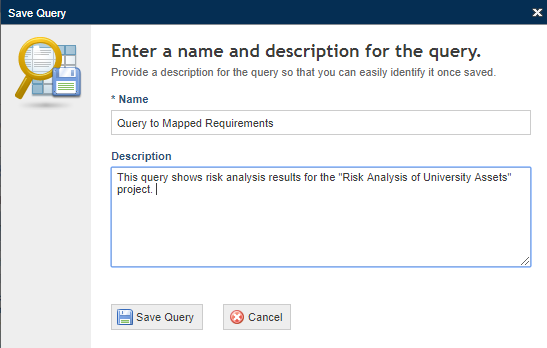
28. In the Name field, enter a name to identify the purpose and reach of the query using up to 50 characters.
29. In the Description field, enter the main characteristics of the query using up to 4,000 characters.
30. When finished, click Save Query. If you want to quit the operation, click Cancel.
The system displays a success message.